Can a dentist pull a problem tooth out? Certainly. But that’s not usually the first option. Having an infected tooth is never a good thing, but modern dentistry does provide several potential solutions.
The most important thing is getting an infected tooth treated sooner than later. Ideally, antibiotics or a root canal can eliminate the infection before more serious measures need to be taken. We’re going to discuss how to tell if you have a tooth infection and what types of treatments are available.
Keeping up with good oral hygiene is an easy way to help prevent a tooth infection. Combined with regular dental exams and cleanings, most people can avoid infections in their teeth and gums by brushing every day.
But if you show the symptoms of an infected tooth make sure to book an appointment before further health detriments occur.
What is an Abscessed Tooth?
An abscessed tooth is a tooth that has a bacterial infection in or around it. A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus that forms at the tooth. This can be painful and dangerous when left untreated.
A dental abscess occurs most commonly in these forms:
- Periapical abscess, at the tip of a tooth’s root.
- Periodontal abscess is an abscess on the gum next to a tooth root that can spread to the surrounding tissue and bone.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
The symptoms of a tooth abscess are quite noticeable as the bacterial infection develops. An obvious symptom is acute pain in and around the abscessed tooth. Pain is often throbbing and intense and can amplify suddenly.
Other symptoms associated with an abscessed tooth include:
- Pain in your ears, jaw, or neck
- Pain that intensifies when lying down
- Pain when chewing or biting
- Facial redness and swelling
- Swollen, red gums
- Tooth sensitivity
- Discoloured or loose teeth
- Bad breath
- Foul taste in your mouth
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
Causes of Tooth Abscesses
The reason for a tooth abscess occurring is bacteria infecting your gums or tooth. Each type of abscess has a specific cause:
- Periapical abscess: bacteria comes in contact with the dental pulp inside your teeth. This is usually due to a deep cavity, cracked tooth or trauma.
- Periodontal abscess: most often the result of gum disease, but can be credited to a dental injury or foreign object gets embedded in your gums (such as a popcorn kernel or toothpick splinter).
Risk Factors for Tooth Infection
Because a tooth abscess can be the result of bacteria penetrating the inside of your tooth, it’s important to protect your tooth enamel. The following can all contribute to a higher chance of tooth abscess:
- Poor oral hygiene
- High-sugar diet
- Large fillings on teeth
- Dry mouth
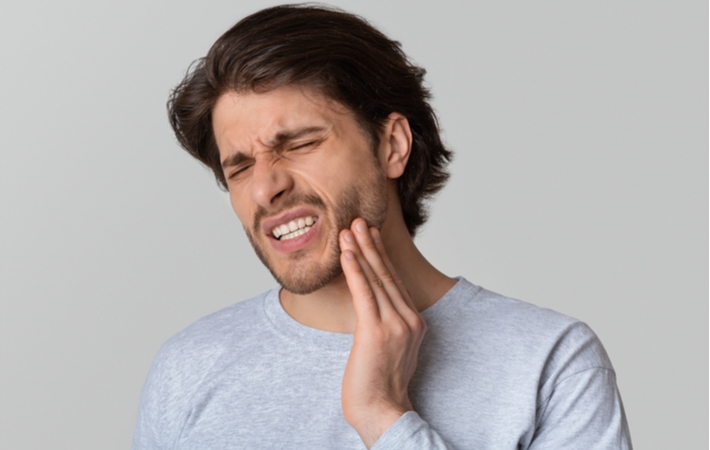

The Importance of Tooth Infection Treatment
A tooth infection or dental abscess is not something to be ignored. The symptoms may be bearable at the onset of infection but will become more painful and noticeable over time. But it’s the spread of infection that makes a tooth abscess so dangerous.
As recent as the early 1900s, tooth infections killed 10 to 40% of those diagnosed. Advances in dentistry have lowered those numbers but a tooth infection left unattended can spread into your jaw, head, neck, heart and other parts of your body. Untreated tooth abscess complications include sepsis, bone infections, soft tissue death, and even brain infections.
Tooth abscess symptoms are meant to warn your body that something is wrong. And treating an abscessed tooth early decreases the risk of necessary tooth extraction. It is indeed wise to be obsessed with treating your abscess.
To Pull or Not To Pull?
When a tooth abscess is recognized early and treated swiftly, the long-term effects are often diminished. But when an infection has become more established, your dentist may require x-rays and a CT scan to ensure it has not spread.
When you’re feeling the pain and other associated symptoms of a tooth abscess it’s always best to visit your dentist immediately.
Abscess Draining
This process involves draining the pus-filled abscess and removing bacterial fluid. A small cut is made near the tooth and the area is drained and washed. With the help of antibiotics, your tooth may be able to fully recover.
The abscess is caused by an embedded foreign object, it will be removed during this process.
Root Canal
When an infected tooth requires more intensive treatment but does not need to be completely removed, your dentist may opt for a root canal.
A root canal requires drilling into the affected tooth and removing any infected dental tissue. Again, the abscess is drained and this space inside your tooth will be filled. The tooth is then sealed and often crowned to complete the root canal procedure.
A successful root canal removes the abscess and infection while allowing you to keep your natural tooth.
Pull The Tooth
When the abscessed tooth has become too damaged or there are severe complications related to the infection, you may require a tooth extraction. In these circumstances, the tooth is completely removed and then the abscess is drained.
Usually, a tooth extraction occurs when a patient neglects an abscessed tooth for too long. It must be pulled, but many patients elect for restorative dentistry to replace the function and aesthetic of the original tooth.
Keeping up with semi-annual dental exams helps prevent an abscess from needing this type of treatment. Antibiotics are often prescribed to prevent the spread of infection during recovery.
Staying Ahead of Infection
So not every infected tooth needs to be removed. Tooth extraction is usually a last resort for both you and your dentist. Although pulling a tooth is always an option, root canals and abscess draining are the preferred treatments. Staying ahead of tooth infection and tooth decay requires diligence in your oral health routine and consistent visits to your dentist. If biannual sessions in the dentist chair seem inconvenient, just remember that ignoring the symptoms of tooth infection can lead to more troublesome activity.